Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery that count change how we go understand the Birth of planetsUsing the european southern observator’s Very large telescope (Vlt) in chile, researchers have found a young plan, named Wispit 2bOrbiting a star Around 430 light years Away. What makes this so special is that the planet sits inside a multi-ringed Protoplanetary disk -a dusty, gas-filled structure where planets form. This is the first confirmed detection of its Kind, and It Offers Scientists a Rare Glimpse ITO How Planetary Systems, Including Our Own System, MAY HAVE Developed Bills of thousands AGE. The team’s research was published across two papers in The astrophysical journey letters,
About the Young Planet Five Times Bigger Than Jupiter: Wispit 2B
Wispit 2b is a Gas Giant Planet, Thought to be about the size of Jupiter but Much Younger – Only 5 million years old. In cosmic terms, that makes it an infant compared to earth’s solar system, which is around 4.6 billion years old. Despite Its Youth, Wispit 2b is alredy massive, estimated to be up to five times bigger than Jupiter. Because it is still forming, the planet glows fantly from the heat of its creation, making it visible in infrared light.
How Astronomers Captured The First Images of Wispit 2B’s Multi-Ringed Disk
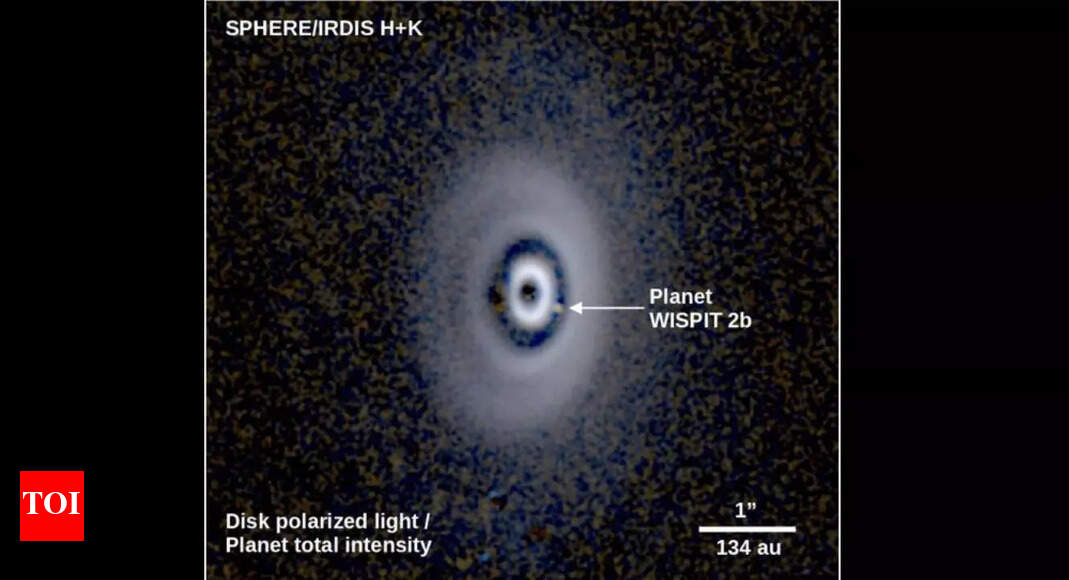
Researchers used the very large telescope (VLT) in the Atacama Desert of Chile to Capture Images of Wispit 2B. At first, they were only conducting short “snapshot” observations of many young stars, hoping to spot planets. INTEAD, they noticed a beautiful multi-ringed disk Around Wispit 2. Follow-up observations confirmed the glowing presence of wispit 2B within one of the disk’s gaps. Later, astronomers from the university of arizona captured images in visible light, proving that the planet is stiff is actively gathering material.
Wispit 2B Discovery Reveals How Young Planets Shape Their Surroundings
Wispit 2b was discovered inside a multi-ringed protoplanetary disk-a structure of gas and dust that orbits young stars and serves as the birthplace of planets. While Astronomers Have Observed Hundreds of Such Disks, Spotting a Planet Clearly Within One is ExTREMELY RARE. Wispit 2b is the first confirmed planet inside a disk with multiple gaps and rings, making it a unique options to study how planets shape and interact with their surroundings.This discovery may also also shed light on how our own Solar System Formed 4.5 Billion Years ago. The disk Around wispit 2 spans about 380 times the Earth – Sun Distance, with WITH WISPIT 2B Carving Visible Channels through the dust. These features provide scientists with Valuable Clues About How Young Planets Clear Paths in their birth environments, Simlar to the Early Processes that shaped Earth, Jupiter, Jupiter, and the Phoanets in our solar System.
What is a protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is like a cosmic nursery. It forms when Gas and dust left over from star formation gather into a huge, spinning disk. Inside this disk, clumps of material stick togetra, growing into planets. Many disks show gaps and rings, which Sugged planets are forming and pulling material legs themselves. Until recently, most of this was theory. Now, with wispit 2b, scientists have directed proof of a young plan at work inside a disk.
Exoplanets EXPLAINED: What makes wispit 2b so special
Exoplanets Are planets that orbit stars outside our solar system. More than 5,800 exoplanets have been discovered so far, and astronomers believe billions more exist in our galaxy alone. Some Exoplanets are Rocky Like Earth, While others are giant Gas Worlds Like Jupiter. Wispit 2b is especially Valuable because it shows us what planets look like in their earliest stages of growth, somenting rarely observed until no.
A rare benchmark system: What Wispit 2B Reveals About Planets
Astronomers call this system a “Benchmark” for planet formation Studies. Wispit 2 is similar to our sun but much younger, making it a perfect test case to compare with how Earth’s Solar System Evolved. Capturing Direct Images of Such Young Planets is Incredible Challenging, which is why scientists are thrled. According to the research team, this discovery will guide future studies and may even explain why other planetary systems look so different from our Own.Also read | 10 fascinating facts about the milky way galaxy